科研绘图sci画图作图学术杂志封面设计toc示意图文章配图医学动画
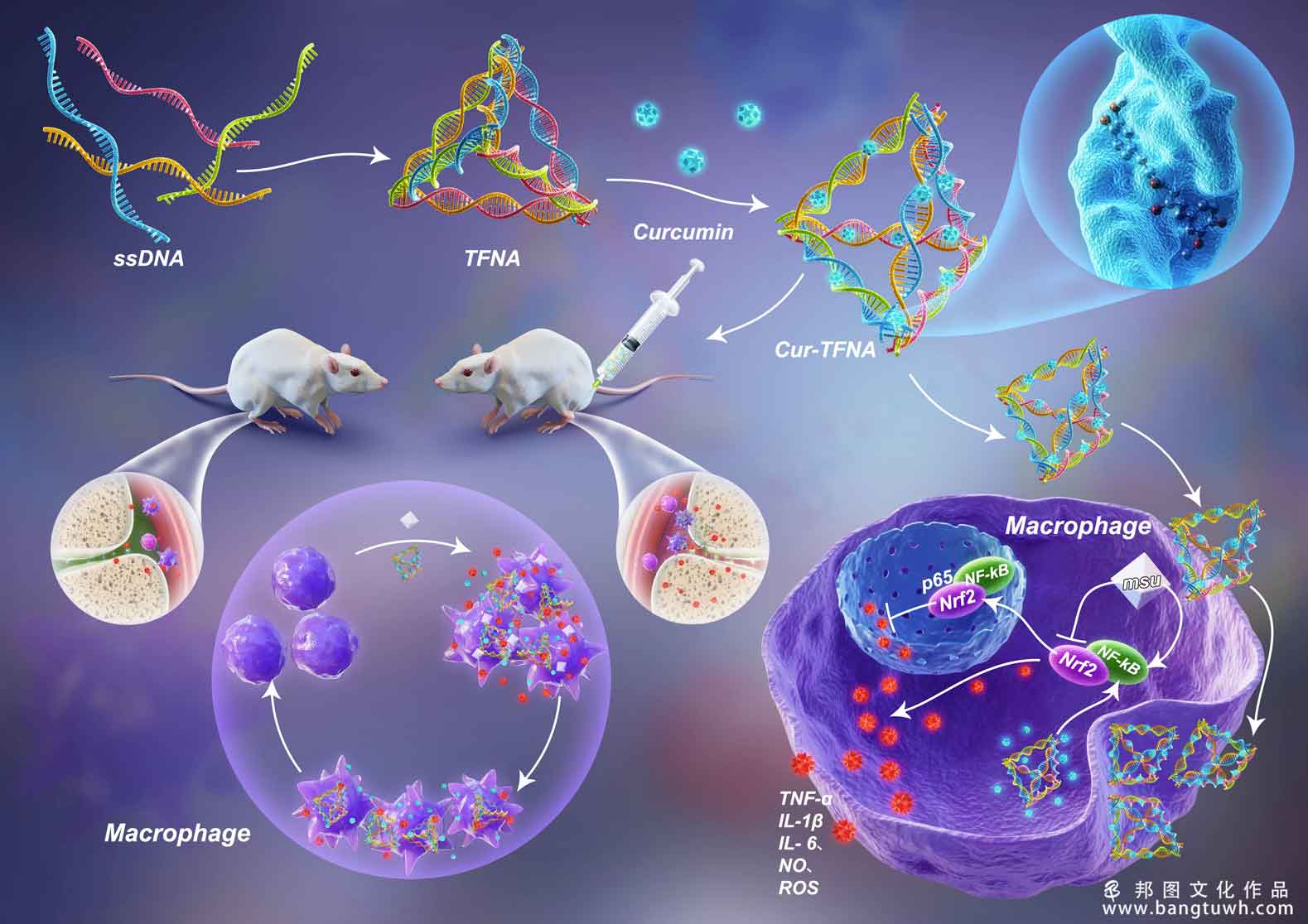


gouty arthritis is a very familiar inflammatory arthritis. controlling inflammation is the key to preventing gouty arthritis. however, colchicine, the most highly represented drug used in clinical practice, has strict contraindications owing to some severe side effects. curcumin (cur), a natural anti-inflammatory drug, has demonstrated good safety and efficacy. however, the rapid degradation, poor aqueous solubility, and low bioavailability of cur limit its therapeutic effect. to strengthen the effectiveness and bioavailability of cur. cur loaded tetrahedral framework nucleic acids (cur-tfnas) were synthesized to deliver cur. compared with free cur, cur-tfnas exhibit a preferable drug stability, good biocompatibility (cck-8 assay), ease of uptake (immunofluorescence), and higher tissue utilization (in vivo biodistribution). most importantly, cur-tfnas present better anti-inflammatory effect than free cur both in vivo and in vitro experiments through the determination of inflammation-related cytokines expression. therefore, we believe that cur-tfnas have great prospects for the prevention of gout and similar inflammatory diseases.



微信扫一扫,加设计师好友
17621261539
周一至周五8:30-18:00

提升“研值”

工作人员将在1个小时内联系您。


