科研绘图sci画图作图学术杂志封面设计toc示意图文章配图医学动画
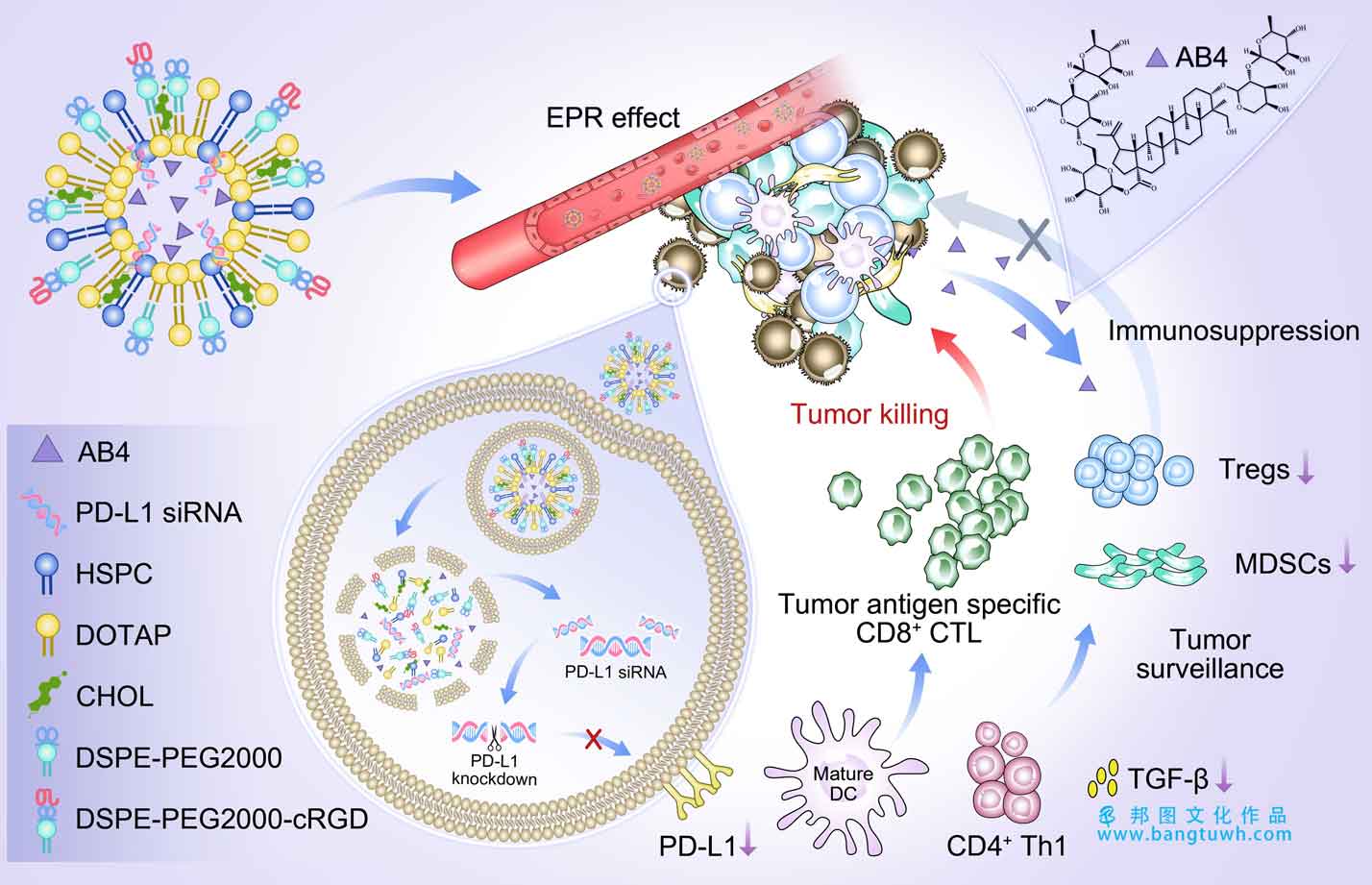


combination therapy has gained a lot of attention thanks to its superior activity against cancer. in the present study, we report a crgd-targeted liposomal preparation for co-delivery of programmed cell death ligand 1 (pd-l1) small interfering rna (sirna) and anemoside b4 (ab4)─ab4/sip-c-l─and evaluate its anticancer efficiency in mouse models of llc and 4t1 tumors. ab4/sip-c-l showed a particle size of (180.7 ± 7.3) nm and a ζ-potential of (32.8 ± 1.5) mv, with high drug encapsulation, ph-sensitive release properties, and good stability in serum. ab4/sip-c-l demonstrated prolonged blood circulation and increased tumor accumulation. elevated cellular uptake was dependent on the targeting ligand crgd. this combination induced significant tumor inhibition in llc xenograft tumor-bearing mice by downregulating pd-l1 protein expression and modulating the immunosuppressive microenvironment. liposomes favored the antitumor t-cell response with long-term memory, without obvious toxicity. a similar tumor growth inhibition was also demonstrated in the 4t1 tumor model. in summary, our results indicate that crgd-modified and ab4- and pd-l1 sirna-coloaded liposomes have potential as an antitumor preparation, and this approach may lay a foundation for the development of a new targeted drug delivery system.



微信扫一扫,加设计师好友
17621261539
周一至周五8:30-18:00

提升“研值”

工作人员将在1个小时内联系您。


